 |
libmpix
The open imaging DSP library
|
 |
libmpix
The open imaging DSP library
|
Convert images from raw Bayer formats to RGB.
Debayering an essential task of any image processing system, due to how image sensors are able to perceive colors.
Most image sensors targetting embedded systems are able to do debayer on their own and the image arrives immediately in RGB565 or YUYV format, so no need to perform debayer in such case.
However, image sensors that performing debayer on their own have more noise defects (due to the heat and digital noise this causes. the image quality can be better for sensors that produce raw frames, and let their controlling chip perform debayer instead.
Furthermore, raw bayer data (often 8 bit/pixel) is typically smaller than decoded data (often 16 bit/pixel).
Some image sensors can also sense infra-red and many other wavelength such as the case of hyperspectral image sensors.
Adding support in software is easier than hardware as every stage is reconfigurable without requiring new chips, and RGB-IR support can easily be added to libmpix on request.
A black and white image sensor does not make any distinction between the wavelength (color) of light and every cell receives the full spectrum information: no distinction between colors.
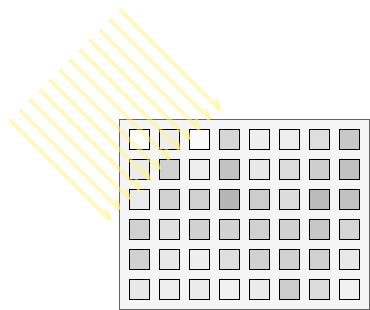
In order to sense each particular color, filters need to be added so that some image cells can be sensitive to just one color information such as the red, green or blue wavelength
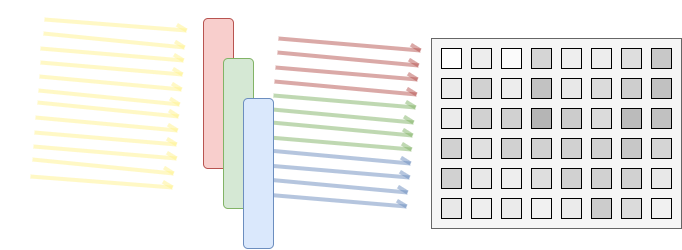
But the filter has to be aligned with every pixel so that it is possible to give each pixel an unique color. And with a well-known pattern to assign each pixel is to a known color R, G or B. The most widespread pattern is the Bayer pattern:
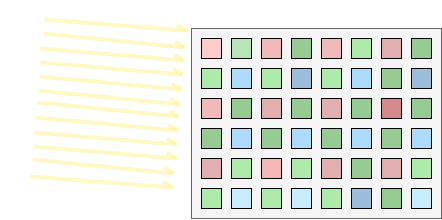
Once the data arrives to the MCU, it is not in RGB format but in grayscale, and by knowing the position of the bayer filter, it is possible to reconstitute the RGB data. This process is called debayer.
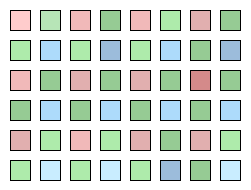
The name of the bayer format is obtained by looking at the order of colors in a bayer image:
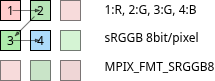
Then the image is imported from a buffer or another source using this format.
There are multiple strategies to implement the debayer operation:
Knowing this, it is now possible to choose a debayer operation, such as 2x2:
The data will then be in MPIX_FMT_RGB24 format and processing can continue in RGB.